Pushing Custom Images to Docker Hub Using GitHub Actions
Automate Docker image builds and deployments with GitHub Actions. This guide shows how to set up CI/CD workflows to build, tag, and push container images to Docker Hub when code changes are committed.
Introduction
Automating Docker image builds and deployments can significantly improve development workflows. This article demonstrates how to use GitHub Actions to automatically build and push Docker images to Docker Hub whenever changes are committed to your repository, saving time and ensuring consistent builds across your team.
Automate docker image build, tag and push to container registry
In the previous article, we explained how to manually push custom Docker images to Docker Hub using the Docker CLI. Now, we’ll streamline that process with automation through GitHub Actions. This guide walks you through setting up a workflow that builds, tags, and pushes Docker images to Docker Hub each time you push changes to the repository.
1. Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure you have:
An application already Dockerized. For example, use a simple setup with two files:
index.htmlandDockerfile. You can find the example project here on GitHub.A Docker Hub account with your username and access token.
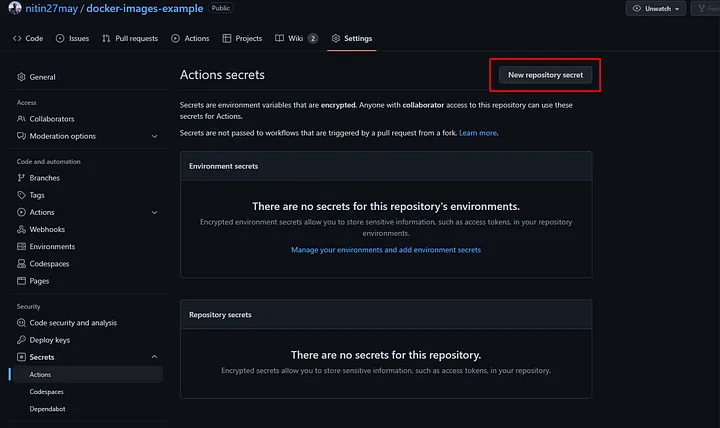
2. Adding Secrets in GitHub
To store your Docker Hub credentials securely, add them as GitHub secrets:
In your GitHub repository, navigate to Settings > Secrets > Actions.
Click New repository secret, name it
DOCKERHUB_TOKEN, and add your Docker Hub access token.
Create a secret named
DOCKERHUB_TOKENand add your Docker Hub access token as the value.Similarly, create a secret named
DOCKERHUB_USERNAMEand add your Docker Hub username.
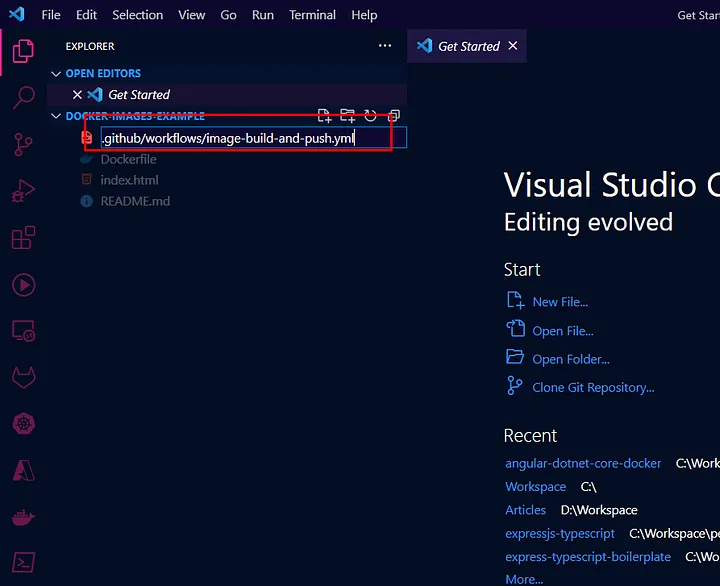
Now let’s add our first GitHub Action at root of our project like below :
3. Setting Up the GitHub Actions Workflow
To automate the process, create a GitHub Actions workflow file in your repository’s root.
Create a new file at .github/workflows/docker-image.yml with the following contents:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
name: Nginx Build
on:
push:
branches: master
paths:
- '**'
jobs:
main:
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
steps:
-
name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
-
name: Set up QEMU
uses: docker/setup-qemu-action@v2
-
name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
-
name: Login to DockerHub
uses: docker/login-action@v2
with:
username: $
password: $
-
name: Build and push
id: docker_build
uses: docker/build-push-action@v3
with:
context: .
file: Dockerfile
push: true
tags: $/my-custom-nginx:latest, $/my-custom-nginx:$
secrets: |
GIT_AUTH_TOKEN=$
-
name: Image digest
run: echo $
This workflow runs each time code is pushed to the master branch:
Checkout: Pulls the latest code from the repository.
Set up QEMU: Installs QEMU for building images for different architectures.
Set up Docker Buildx: Enables advanced build options in Docker.
Log in to Docker Hub: Uses your stored credentials to log in.
Build and Push Image: Builds the image and tags it with both
latestand the GitHub Run Number for unique builds.Show Image Digest: Outputs the digest after a successful build.
4. Tagging the Docker Image
The workflow tags the image in two ways:
latest: This tag will always point to the most recent image.$: This is a unique tag based on the GitHub Actions run number, which ensures that each build has its own version tag.
5. Monitoring the Workflow
Once you push the workflow file to the master branch, GitHub Actions automatically triggers the build. You can view the status under the repository’s Actions tab. A yellow dot shows a build in progress, and tags are updated upon successful completion.
The below screenshot shows how tags get updated in any build.
Below is the screenshot from a successful run.
6. Viewing the Results
When the image is pushed to Docker Hub, you’ll see both latest and unique version tags (e.g., 5). This feature allows easy version control and retrieval of specific image versions.
Here’s a screenshot of the published image tags:sccessful push, we can see that it pushed 2 tags, one is latest and another is 5, which we can see that it was the build number.
Conclusion
This article demonstrated how to automate Docker image build, tag, and push to Docker Hub using GitHub Actions. This workflow enhances efficiency by keeping Docker images up to date with every code push to the master branch. In the next article, we’ll explore automation with different cloud container registries.
Thank you for reading!
Get Involved
- Follow for Updates: Follow to stay informed about the latest developer tools and cloud development practices.