Backend Documentation
Overview
The backend of this project is built with .NET 10, following Clean Architecture principles. It provides a robust API layer for the Angular frontend, using Dapper for efficient data access and PostgreSQL 17 as the database. API documentation is provided via Scalar (replacing Swagger/Swashbuckle).
Technology Stack
- .NET 10
- ASP.NET Core Web API
- Minimal API approach where applicable
- Modern dependency injection system
- Middleware pipeline
- .NET Aspire 9.5 for orchestration
- Data Access
- Dapper for efficient data access
- PostgreSQL 17 database
- Generic Repository pattern
- Unit of Work for transaction management
- Authentication & Authorization
- JWT token authentication
- Role-based authorization
- Policy-based access control
- Password hashing and security
- Validation & Mapping
- FluentValidation for request validation
- AutoMapper for object mapping
- DTO pattern for data transfer
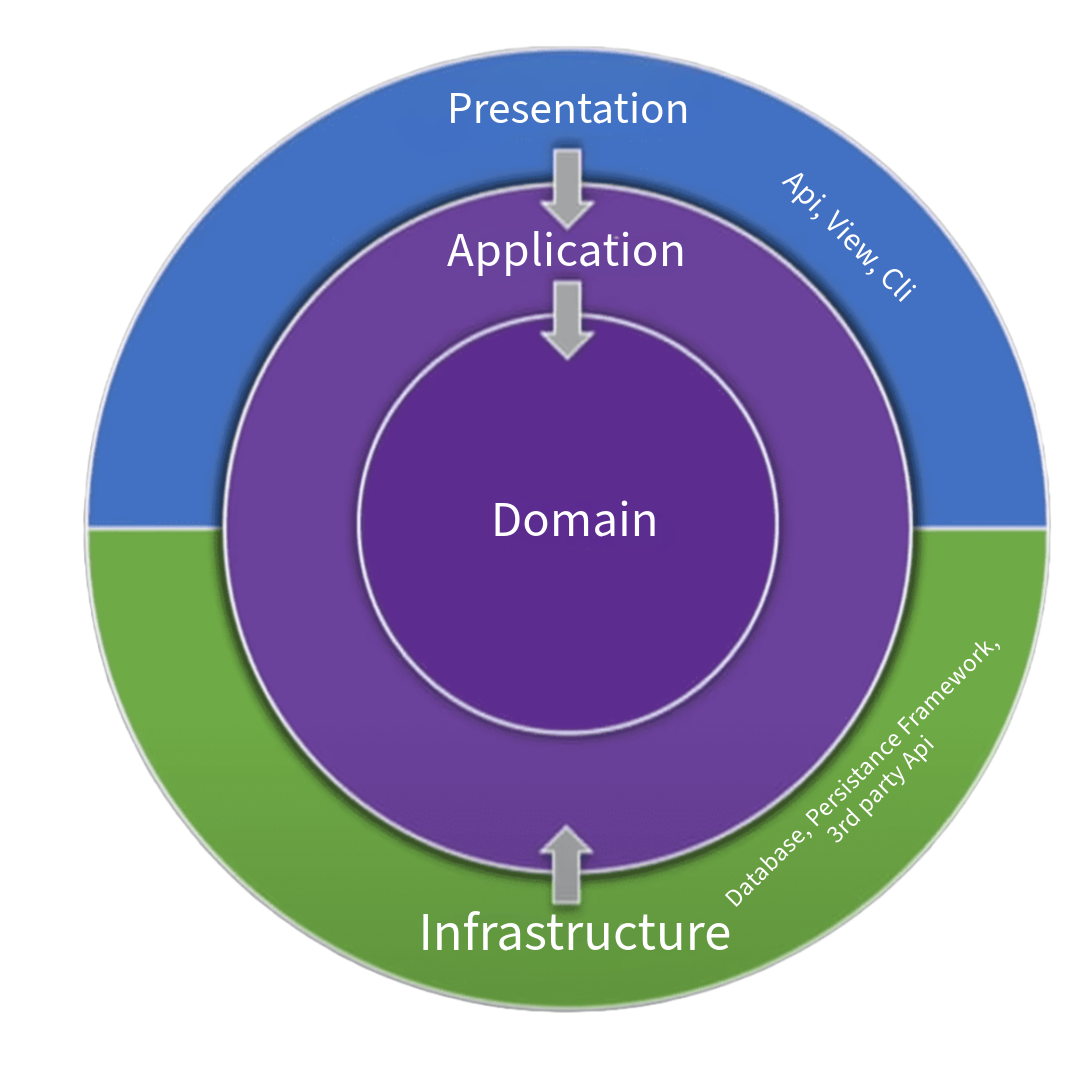
Clean Architecture Layers
The backend follows Clean Architecture with four distinct layers:
1. Domain Layer
The core of the application, containing:
- Business entities
- Value objects
- Domain events
- Domain exceptions
- Domain interfaces
This layer has no dependencies on other layers or external frameworks.
// Domain Entity Example
namespace Contact.Domain.Entities
{
public class ContactPerson : BaseEntity
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public DateTime? DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public int? CountryCode { get; set; }
public long? Mobile { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string PostalCode { get; set; }
}
}
2. Application Layer
Contains the business logic and orchestrates the domain objects:
- Application services
- Command and query handlers
- DTO (Data Transfer Objects)
- Interfaces for infrastructure services
- Validation logic
// Application Service Example
namespace Contact.Application.Services
{
public class ContactPersonService : GenericService<ContactPerson, ContactPersonResponse, CreateContactPerson, UpdateContactPerson>, IContactPersonService
{
private readonly IGenericRepository<ContactPerson> _contactPersonRepository;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
public ContactPersonService(
IGenericRepository<ContactPerson> contactPersonRepository,
IMapper mapper,
IUnitOfWork unitOfWork) : base(contactPersonRepository, mapper, unitOfWork)
{
_contactPersonRepository = contactPersonRepository;
_mapper = mapper;
_unitOfWork = unitOfWork;
}
// Specialized methods beyond CRUD operations
}
}
3. Infrastructure Layer
Implements interfaces defined in the domain and application layers:
- Database access with Dapper and PostgreSQL
- External service integrations
- File storage implementations
- Email service implementation
- Logging implementations
// Repository Implementation Example
namespace Contact.Infrastructure.Persistence.Repositories
{
public class ContactPersonRepository : GenericRepository<ContactPerson>
{
public ContactPersonRepository(IDapperHelper dapperHelper)
: base(dapperHelper, "Contacts")
{
}
// Custom query methods specific to ContactPerson
public async Task<IEnumerable<ContactPerson>> SearchByName(string searchTerm)
{
var query = @"SELECT * FROM ""Contacts""
WHERE ""FirstName"" ILIKE @SearchTerm
OR ""LastName"" ILIKE @SearchTerm";
var parameters = new { SearchTerm = $"%{searchTerm}%" };
return await _dapperHelper.ExecuteQuery<ContactPerson>(query, parameters);
}
}
}
4. API Layer
The entry point to the application:
- API controllers and endpoints
- Request/response models
- API-specific mappings
- Middleware configuration
- Authentication setup
- Swagger/OpenAPI documentation
// API Controller Example
namespace Contact.Api.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ContactPersonController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IContactPersonService _contactPersonService;
private readonly ILogger<ContactPersonController> _logger;
public ContactPersonController(
IContactPersonService contactPersonService,
ILogger<ContactPersonController> logger)
{
_contactPersonService = contactPersonService;
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpGet]
[ActivityLog("Getting Contact List")]
[AuthorizePermission("Contacts.Read")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get()
{
var contactPeople = await _contactPersonService.GetAll();
return Ok(contactPeople);
}
// Other CRUD endpoints
}
}
API Documentation with Scalar
The API is documented using Scalar, a modern API documentation tool that replaces Swagger UI:
API documentation with Scalar available at /scalar/v1 endpoint
// Scalar Configuration in Program.cs
builder.Services.AddOpenApi();
// In the middleware pipeline
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.MapOpenApi();
app.MapScalarApiReference(options =>
{
options
.WithTitle("Contact API")
.WithPreferredScheme("Bearer")
.WithHttpBearerAuthentication(bearer =>
{
bearer.Token = "your-jwt-token";
});
});
}
Key Design Patterns
Generic Repository Pattern
The solution implements a generic repository pattern for data access:
public interface IGenericRepository<T> where T : BaseEntity
{
Task<T> Add(T item, IDbTransaction? transaction = null);
Task<bool> Delete(Guid id);
Task<T> Update(T item, IDbTransaction? transaction = null);
Task<T> FindByID(Guid id);
Task<IEnumerable<T>> Find(string query, object? parameters = null);
Task<IEnumerable<T>> FindAll();
}
public class GenericRepository<T> : IGenericRepository<T> where T : BaseEntity
{
protected readonly IDapperHelper _dapperHelper;
protected readonly string _tableName;
public GenericRepository(IDapperHelper dapperHelper, string tableName)
{
_dapperHelper = dapperHelper;
_tableName = tableName;
}
public async Task<T> Add(T item, IDbTransaction? transaction = null)
{
var properties = typeof(T).GetProperties()
.Where(p => p.Name != "Id" && !p.Name.EndsWith("Id") && p.GetValue(item) != null)
.ToList();
var columns = string.Join(", ", properties.Select(p => $"\"{p.Name}\""));
var parameters = string.Join(", ", properties.Select(p => $"@{p.Name}"));
var query = $@"
INSERT INTO ""{_tableName}"" ({columns})
VALUES ({parameters})
RETURNING *";
var result = await _dapperHelper.ExecuteScalarAsync<T>(query, item, transaction);
return result;
}
// Other implementation methods...
}
Generic Service Pattern
Services follow a generic pattern for common operations:
public class GenericService<TEntity, TResponse, TCreate, TUpdate>
: IGenericService<TEntity, TResponse, TCreate, TUpdate>
where TEntity : BaseEntity
where TResponse : class
where TCreate : class
where TUpdate : class
{
private readonly IGenericRepository<TEntity> _repository;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
public GenericService(IGenericRepository<TEntity> repository, IMapper mapper, IUnitOfWork unitOfWork)
{
_repository = repository;
_mapper = mapper;
_unitOfWork = unitOfWork;
}
public async Task<TResponse> Add(TCreate createDto)
{
var transaction = _unitOfWork.BeginTransaction();
try
{
var entity = _mapper.Map<TEntity>(createDto);
var result = await _repository.Add(entity, transaction);
_unitOfWork.Commit();
return _mapper.Map<TResponse>(result);
}
catch
{
_unitOfWork.Rollback();
throw;
}
}
// Other implementation methods...
}
Unit of Work Pattern
For transaction management:
public interface IUnitOfWork : IDisposable
{
IDbTransaction BeginTransaction();
void Commit();
void Rollback();
Task<T> ExecuteInTransactionAsync<T>(Func<IDbTransaction, Task<T>> operation);
}
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork
{
private readonly IDapperHelper _dapperHelper;
private IDbTransaction _transaction;
private IDbConnection _connection;
private bool _disposed;
public UnitOfWork(IDapperHelper dapperHelper)
{
_dapperHelper = dapperHelper;
_connection = _dapperHelper.GetConnection();
}
public IDbTransaction BeginTransaction()
{
if (_connection.State == ConnectionState.Closed)
_connection.Open();
_transaction = _connection.BeginTransaction();
return _transaction;
}
public void Commit()
{
try
{
_transaction?.Commit();
}
catch
{
_transaction?.Rollback();
throw;
}
finally
{
_transaction?.Dispose();
_transaction = null;
}
}
public void Rollback()
{
try
{
_transaction?.Rollback();
}
finally
{
_transaction?.Dispose();
_transaction = null;
}
}
// Other implementation methods...
}
Authentication System
The application uses JWT-based authentication with role-based authorization:
public async Task<AuthenticateResponse> Authenticate(AuthenticateRequest authenticateRequest)
{
var user = await _userRepository.FindByUserName(authenticateRequest.Username);
if (user == null)
{
var failedResponse = new AuthenticateResponse()
{
Authenticate = false
};
return failedResponse;
}
var passwordHasher = new PasswordHasher<string>();
var result = passwordHasher.VerifyHashedPassword(
user.Email,
user.Password,
authenticateRequest.Password
);
if (result == PasswordVerificationResult.Failed)
{
var failedResponse = new AuthenticateResponse()
{
Authenticate = false
};
return failedResponse;
}
var token = await GenerateJwtToken(user);
var response = new AuthenticateResponse
{
Authenticate = true,
Id = user.Id,
Username = user.Email,
Token = token,
ExpireOn = DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(7)
};
return response;
}
private async Task<string> GenerateJwtToken(User user)
{
var roles = await GetRoles(user);
var claims = new List<Claim>
{
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.Email),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier, user.Id.ToString())
};
// Add roles to claims
foreach (var role in roles)
{
claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, role));
}
var key = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(_appSettings.Secret));
var creds = new SigningCredentials(key, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
var expires = DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(7);
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: _appSettings.ValidIssuer,
audience: _appSettings.ValidAudience,
claims: claims,
expires: expires,
signingCredentials: creds
);
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token);
}
Role-Based Authorization
The backend implements a flexible permission system:
// Custom permission-based authorization attribute
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Class, AllowMultiple = true)]
public class AuthorizePermissionAttribute : AuthorizeAttribute
{
public AuthorizePermissionAttribute(string permission)
{
Policy = permission + "Policy";
}
}
// Permission handler implementation
public class PermissionHandler : AuthorizationHandler<PermissionRequirement>
{
private readonly IServiceProvider _serviceProvider;
public PermissionHandler(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
_serviceProvider = serviceProvider;
}
protected override async Task HandleRequirementAsync(
AuthorizationHandlerContext context,
PermissionRequirement requirement)
{
using (var scope = _serviceProvider.CreateScope())
{
var _userService = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IUserService>();
var _rolePermissionService = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IRolePermissionService>();
if (context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
var userId = _userService.GetUserId(context.User);
var roles = await _userService.GetUserRolesAsync(context.User);
var rolePermissionMappings = await _rolePermissionService.GetRolePermissionMappingsAsync();
var userPermissions = rolePermissionMappings
.Where(rpm => roles.Contains(rpm.RoleName))
.Select(rpm => $"{rpm.PageName}.{rpm.OperationName}Policy");
if (userPermissions.Contains(requirement.Permission))
{
context.Succeed(requirement);
}
else
{
context.Fail();
}
}
}
}
}
API Features
Global Error Handling
Centralized error handling with middleware:
public class ExceptionMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly ILogger<ExceptionMiddleware> _logger;
public ExceptionMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILogger<ExceptionMiddleware> logger)
{
_next = next;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
try
{
await _next(context);
}
catch (ValidationException ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Validation error: {ex}");
await HandleValidationExceptionAsync(context, ex);
}
catch (DomainException ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Domain error: {ex}");
await HandleDomainExceptionAsync(context, ex);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Unhandled error: {ex}");
await HandleExceptionAsync(context, ex);
}
}
private async Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception)
{
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError;
await context.Response.WriteAsync(new ErrorDetails
{
StatusCode = context.Response.StatusCode,
Message = "Internal Server Error. Please try again later."
}.ToString());
}
private async Task HandleValidationExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, ValidationException exception)
{
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest;
var errors = exception.Errors
.GroupBy(e => e.PropertyName)
.ToDictionary(
g => g.Key,
g => g.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage).ToArray()
);
await context.Response.WriteAsync(new ValidationErrorDetails
{
StatusCode = context.Response.StatusCode,
Message = "Validation failed",
Errors = errors
}.ToString());
}
// Other exception handling methods...
}
Activity Logging
Comprehensive activity tracking:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false)]
public class ActivityLogAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Description { get; }
public ActivityLogAttribute(string description)
{
Description = description;
}
}
public class ActivityLoggingMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly ILogger<ActivityLoggingMiddleware> _logger;
private readonly IServiceProvider _serviceProvider;
public ActivityLoggingMiddleware(
RequestDelegate next,
ILogger<ActivityLoggingMiddleware> logger,
IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
_next = next;
_logger = logger;
_serviceProvider = serviceProvider;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
var endpoint = context.GetEndpoint();
var activityAttribute = endpoint?.Metadata.GetMetadata<ActivityLogAttribute>();
if (activityAttribute != null && context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
using (var scope = _serviceProvider.CreateScope())
{
var activityService = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IActivityLogService>();
var userService = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IUserService>();
var userId = userService.GetUserId(context.User);
var requestPath = context.Request.Path.Value;
var ipAddress = context.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString();
var activity = new ActivityLog
{
UserId = userId,
Description = activityAttribute.Description,
PageAccessed = requestPath,
IPAddress = ipAddress,
ActivityDate = DateTime.UtcNow
};
// Log asynchronously to not delay the response
_ = activityService.LogActivityAsync(activity);
}
}
await _next(context);
}
}
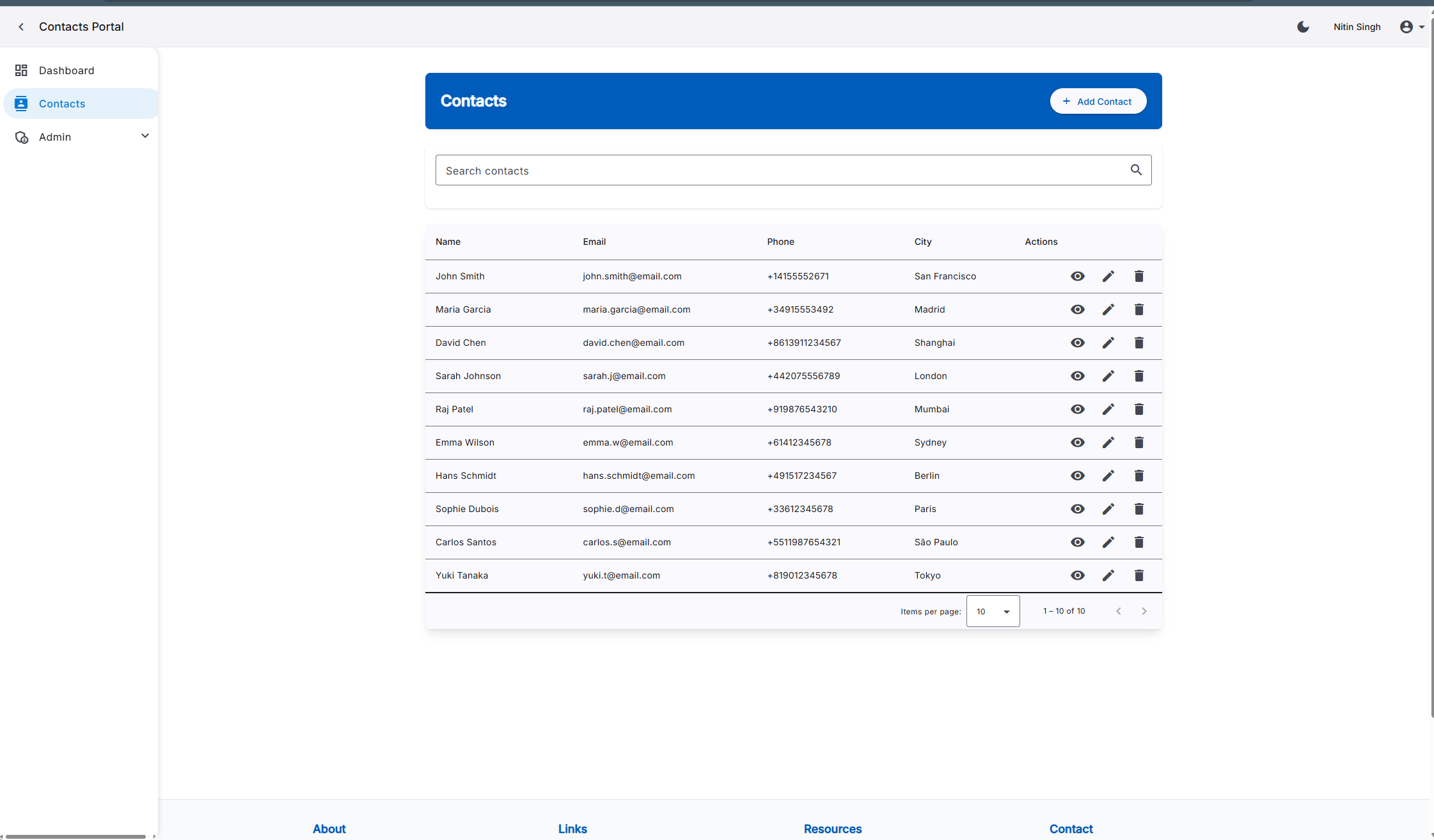
Contact Management API
Complete CRUD operations:
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ContactPersonController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IContactPersonService _contactPersonService;
private readonly ILogger<ContactPersonController> _logger;
public ContactPersonController(
IContactPersonService contactPersonService,
ILogger<ContactPersonController> logger)
{
_contactPersonService = contactPersonService;
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpGet]
[ActivityLog("Getting Contact List")]
[AuthorizePermission("Contacts.Read")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get()
{
var contactPeople = await _contactPersonService.GetAll();
return Ok(contactPeople);
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
[ActivityLog("Getting Contact Details")]
[AuthorizePermission("Contacts.Read")]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetById(Guid id)
{
var contactPerson = await _contactPersonService.GetById(id);
if (contactPerson == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(contactPerson);
}
[HttpPost]
[ActivityLog("Creating new Contact")]
[AuthorizePermission("Contacts.Create")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Add(CreateContactPerson createContactPerson)
{
var createdContactPerson = await _contactPersonService.Add(createContactPerson);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(GetById), new { id = createdContactPerson.Id }, createdContactPerson);
}
[HttpPut("{id}")]
[ActivityLog("Updating Contact")]
[AuthorizePermission("Contacts.Update")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Update(Guid id, UpdateContactPerson updateContactPerson)
{
if (id != updateContactPerson.Id)
{
return BadRequest("ID in URL does not match ID in request body");
}
var updatedContactPerson = await _contactPersonService.Update(updateContactPerson);
return Ok(updatedContactPerson);
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
[ActivityLog("Deleting Contact")]
[AuthorizePermission("Contacts.Delete")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(Guid id)
{
var result = await _contactPersonService.Delete(id);
if (!result)
{
return NotFound();
}
return NoContent();
}
}
Data Seeding
The application includes seed data for essential entities:
-- Insert roles
INSERT INTO "Roles" ("Id", "Name", "Description", "CreatedOn", "CreatedBy") VALUES
('d95d2348-1d79-4b93-96d4-e48e87fcb4b5', 'Admin', 'This is Admin Role', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('3a07551f-7473-44a6-a664-e6c7c834902b', 'Reader', 'This is a Reader role', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('104102f5-e0ec-4739-8fda-f05552b677c3', 'Editor', 'This is editor role', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb');
-- Insert operations
INSERT INTO "Operations" ("Id", "Name", "Description", "CreatedOn", "CreatedBy") VALUES
('d9bcff9c-0ab6-44e4-b9e2-6eed158bd38f', 'Read', 'Read Operation', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('df8a94c9-08d5-4c43-b21e-85d37dd6f264', 'Create', 'Create Operation', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('d5fd3cbe-930c-4151-8965-92c40af5a5f7', 'Update', 'Update Operation', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('458db0c1-b0e0-44b7-bb0b-f49ec9f2f353', 'Delete', 'Delete Operation', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb');
-- Insert pages
INSERT INTO "Pages" ("Id", "Name", "Description", "CreatedOn", "CreatedBy") VALUES
('0830b891-da5e-4a9e-bf32-bd1619758837', 'Users', 'User Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('93d393d0-5424-49ab-8c34-a16a441c0563', 'Role', 'Role Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('dcd5c1b1-ec06-43b5-87ba-a792aa0cc5bf', 'Permission', 'Permission Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('8d2c789d-4aba-4925-9f14-0383c29a77bc', 'Contacts', 'Contact Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('3911eda7-eca0-4b4c-99b5-5aefc49d833d', 'Page', 'Page Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('b5b5d18d-3695-43ad-8632-30d105226b93', 'Operation', 'Operation Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('5a2e8a8d-55fe-4dd9-a27a-f7fd46a4b0ee', 'RolePermission', 'Role Permission Management', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
('8f60c013-6962-43f3-90f6-a4924eb6c992', 'Log', 'Activity Log', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb');
-- Insert sample contacts
INSERT INTO "Contacts" ("Id", "FirstName", "LastName", "DateOfBirth", "CountryCode", "Mobile", "Email", "City", "PostalCode", "CreatedOn", "CreatedBy") VALUES
(uuid_generate_v4(), 'John', 'Smith', '1985-03-15', 1, 4155552671, 'john.smith@email.com', 'San Francisco', '94105', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
(uuid_generate_v4(), 'Maria', 'Garcia', '1990-08-22', 1, 6175556432, 'maria.garcia@email.com', 'Boston', '02108', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb'),
(uuid_generate_v4(), 'David', 'Johnson', '1982-11-07', 1, 3125559087, 'david.johnson@email.com', 'Chicago', '60601', NOW(), '26402b6c-ebdd-44c3-9188-659a134819cb');
Docker Integration
The backend is containerized with Docker for both production and development environments:
# Production Dockerfile
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:10.0 AS base
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 8000
ENV ASPNETCORE_URLS=http://+:8000
RUN groupadd -g 2000 dotnet \
&& useradd -m -u 2000 -g 2000 dotnet
USER dotnet
# Build stage
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:10.0 AS build
ARG BUILD_CONFIGURATION=Release
ARG DOTNET_SKIP_POLICY_LOADING=true
WORKDIR /src
COPY ["Contact.Api/Contact.Api.csproj", "Contact.Api/"]
COPY ["Contact.Application/Contact.Application.csproj", "Contact.Application/"]
COPY ["Contact.Domain/Contact.Domain.csproj", "Contact.Domain/"]
COPY ["Contact.Infrastructure/Contact.Infrastructure.csproj", "Contact.Infrastructure/"]
RUN dotnet restore "Contact.Api/Contact.Api.csproj"
COPY . .
WORKDIR "/src/Contact.Api"
RUN dotnet build "Contact.Api.csproj" -c $BUILD_CONFIGURATION -o /app/build
# Publish stage
FROM build AS publish
ARG BUILD_CONFIGURATION=Release
RUN dotnet publish "Contact.Api.csproj" -c $BUILD_CONFIGURATION -o /app/publish /p:UseAppHost=false
# Final stage
FROM base AS final
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=publish /app/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "Contact.Api.dll"]
# docker-compose.yml excerpt for backend
services:
api:
container_name: api
build:
context: ./backend/src
dockerfile: Dockerfile
ports:
- "8000:8000"
environment:
- ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Development
- ConnectionStrings__DefaultConnection=Host=db;Port=5432;Database=contacts;Username=postgres;Password=password
- JwtSettings__Secret=super-secret-key-for-jwt-token-generation-that-is-long-enough
- JwtSettings__ExpiryMinutes=1440
- JwtSettings__Issuer=ContactApp
- JwtSettings__Audience=ContactAppClients
depends_on:
- db
networks:
- cleanarch-network
db:
container_name: db
image: postgres:16-alpine
ports:
- "5432:5432"
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
- POSTGRES_DB=contacts
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./backend/scripts/seed-data.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/seed-data.sql
networks:
- cleanarch-network
Project Structure
/backend/src
├── Contact.Api # API Layer
│ ├── Controllers/ # API endpoints
│ │ ├── ContactPersonController.cs
│ │ ├── UserController.cs
│ │ ├── RoleController.cs
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── Core/ # Core API functionality
│ │ ├── Attributes/ # Custom attributes
│ │ │ └── ActivityLogAttribute.cs
│ │ ├── Authorization/ # Authorization logic
│ │ │ ├── AuthorizePermissionAttribute.cs
│ │ │ └── PermissionHandler.cs
│ │ └── Middleware/ # API middleware
│ │ ├── ExceptionMiddleware.cs
│ │ └── ActivityLoggingMiddleware.cs
│ └── Program.cs # Application entry point
├── Contact.Application # Application Layer
│ ├── Interfaces/ # Application interfaces
│ │ ├── IContactPersonService.cs
│ │ ├── IUserService.cs
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── Mappings/ # AutoMapper profiles
│ │ └── MappingProfile.cs
│ ├── Services/ # Application services
│ │ ├── ContactPersonService.cs
│ │ ├── UserService.cs
│ │ └── ...
│ └── UseCases/ # Use case DTOs
│ ├── ContactPerson/
│ │ ├── ContactPersonResponse.cs
│ │ ├── CreateContactPerson.cs
│ │ └── UpdateContactPerson.cs
│ └── ...
├── Contact.Domain # Domain Layer
│ ├── Entities/ # Domain entities
│ │ ├── BaseEntity.cs
│ │ ├── ContactPerson.cs
│ │ ├── User.cs
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── Exceptions/ # Domain exceptions
│ │ ├── DomainException.cs
│ │ └── ...
│ └── Interfaces/ # Domain interfaces
│ └── ...
└── Contact.Infrastructure # Infrastructure Layer
├── ExternalServices/ # External API integrations
│ └── ...
├── Persistence/ # Data access
│ ├── Helper/ # Dapper helpers
│ │ ├── DapperHelper.cs
│ │ └── IDapperHelper.cs
│ └── Repositories/ # Repository implementations
│ ├── ContactPersonRepository.cs
│ ├── UserRepository.cs
│ └── ...
└── Services/ # Infrastructure services
└── ...
PostgreSQL Integration
The application uses Npgsql for PostgreSQL database access:
public class DapperHelper : IDapperHelper
{
private readonly AppSettings myConfig;
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public DapperHelper(IOptions<AppSettings> myConfigValue, ILogger<DapperHelper> logger)
{
myConfig = myConfigValue.Value;
_logger = logger;
}
public NpgsqlConnection GetConnection()
{
return new NpgsqlConnection(myConfig.ConnectionStrings.DefaultConnection);
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<T>> ExecuteQuery<T>(string query, object parameters = null, IDbTransaction transaction = null)
{
using var connection = transaction?.Connection ?? GetConnection();
try
{
if (transaction == null && connection.State == ConnectionState.Closed)
connection.Open();
return await connection.QueryAsync<T>(query, parameters, transaction);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error executing query: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
public async Task<T> ExecuteScalarAsync<T>(string query, object parameters = null, IDbTransaction transaction = null)
{
using var connection = transaction?.Connection ?? GetConnection();
try
{
if (transaction == null && connection.State == ConnectionState.Closed)
connection.Open();
return await connection.QueryFirstOrDefaultAsync<T>(query, parameters, transaction);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error executing scalar query: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
public async Task<int> ExecuteAsync(string query, object parameters = null, IDbTransaction transaction = null)
{
using var connection = transaction?.Connection ?? GetConnection();
try
{
if (transaction == null && connection.State == ConnectionState.Closed)
connection.Open();
return await connection.ExecuteAsync(query, parameters, transaction);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error executing command: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
}
Best Practices for Backend Development
When working with the backend codebase, follow these guidelines:
-
Keep domain entities pure: Domain entities should be free from infrastructure concerns and focused on business logic.
- Place business logic in the appropriate layer:
- Domain layer for core business rules
- Application layer for orchestration and use cases
- Infrastructure layer for technical implementations
-
Use proper exception handling: Create domain-specific exceptions and handle them appropriately in the API layer.
-
Validate all incoming requests: Use FluentValidation to validate all incoming DTO objects.
- Follow SOLID principles:
- Single Responsibility Principle
- Open/Closed Principle
- Liskov Substitution Principle
- Interface Segregation Principle
- Dependency Inversion Principle
-
Implement proper logging: Log important events, errors, and performance metrics.
-
Use async/await consistently: Ensure non-blocking code throughout the application.
-
Use transactions for multi-entity operations: Wrap operations that modify multiple entities in transactions.
-
Keep controllers thin: Controllers should only handle HTTP concerns, delegating business logic to services.
-
Follow the established permission model for security: Consistently apply the
[AuthorizePermission]attribute to secure endpoints. -
Use the Generic Repository and Service patterns: Leverage the built-in generic patterns for standard CRUD operations.
- Document APIs with XML comments: Ensure all public APIs are properly documented with XML comments for Swagger.